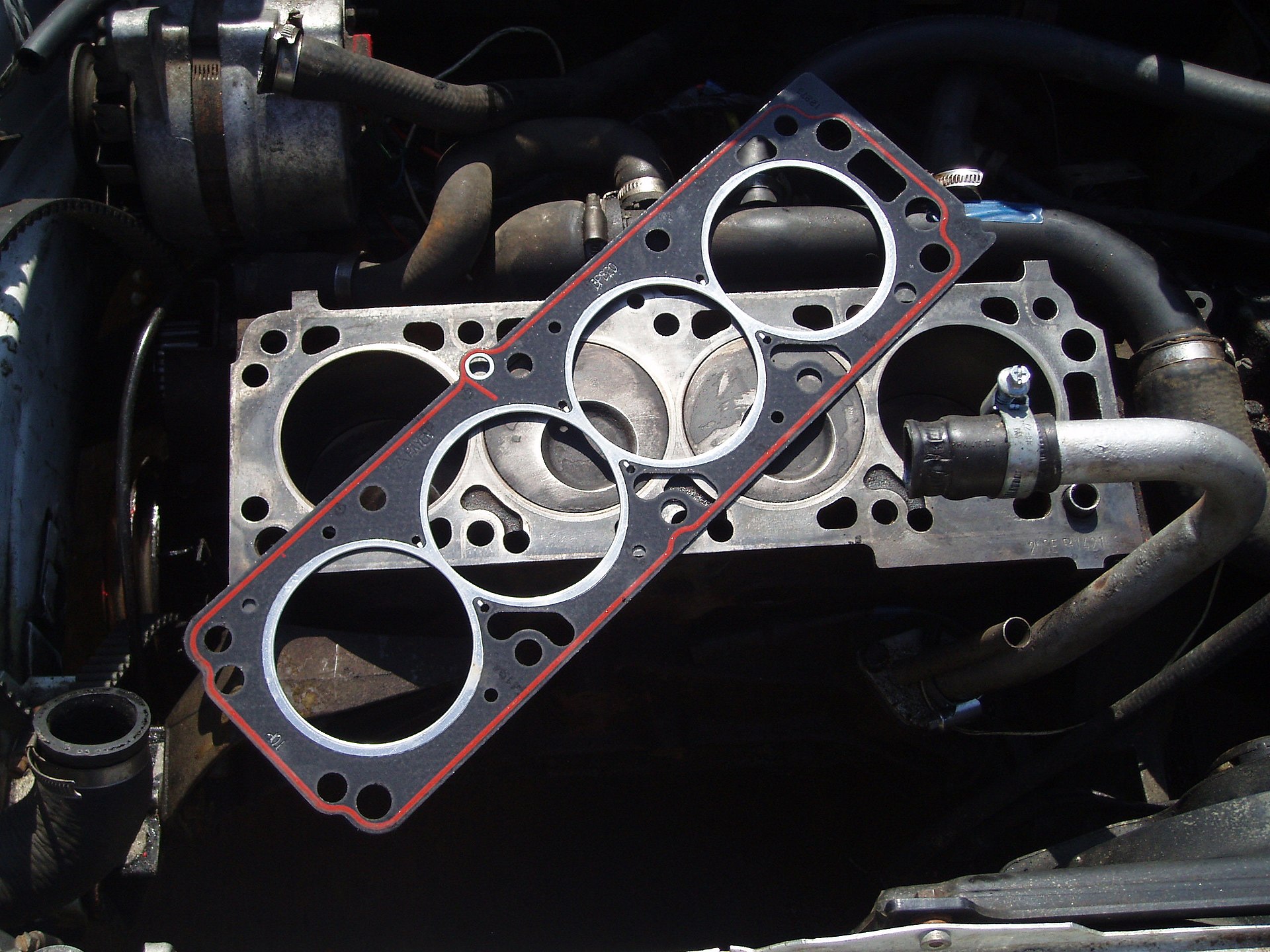
The head gasket plays a pivotal role in the efficient operation of internal combustion engines. It acts as a seal between the engine block and cylinder head, ensuring proper compression while preventing leakage of coolant or oil into the cylinders. This article explores the functions, maintenance, common failures, and repair options for head gaskets, providing useful insights and expert tips.
Functions of the Head Gasket
- Sealing Combustion Chambers: The gasket ensures the high-pressure environment within the cylinders remains intact, preventing power loss.
- Channel Protection: It seals coolant and oil passages, ensuring they don’t mix or leak into unintended areas.
- Heat Transfer: The gasket facilitates even heat distribution between the engine block and cylinder head, reducing hot spots and potential damage.
- Adaptation to Bimetal Stress: Modern engines, often made of aluminum and iron, expand at different rates under heat. The head gasket compensates for this, maintaining a durable seal. Learn more here.
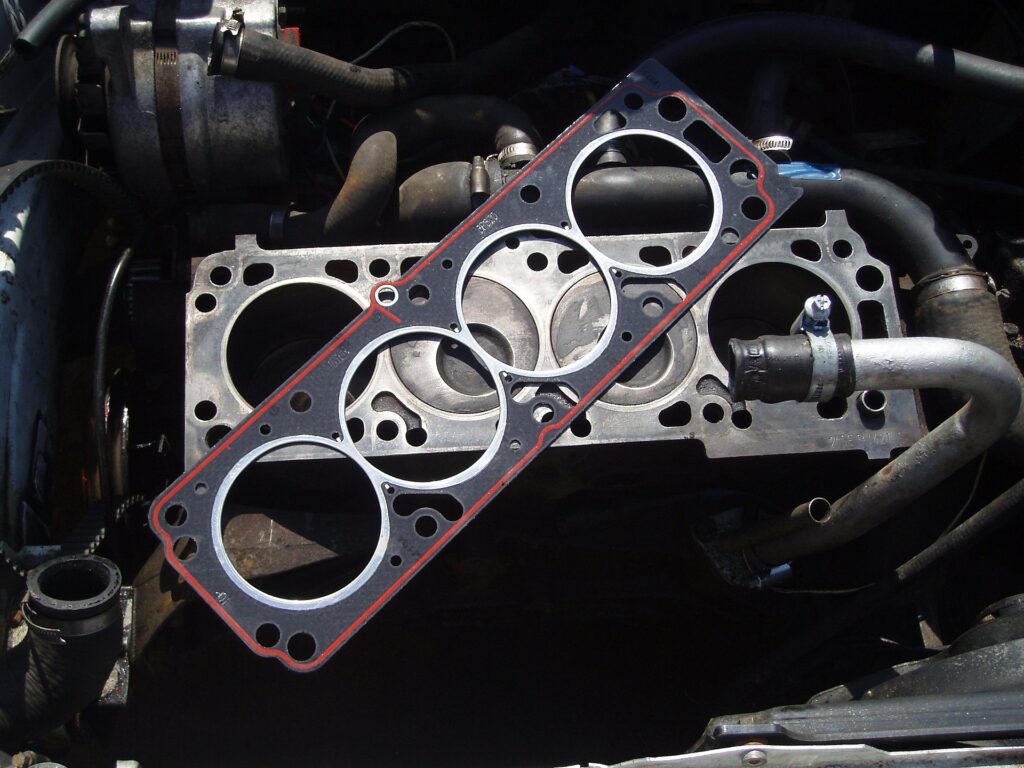
Symptoms of a Blown Head Gasket
Detecting a blown gasket early can save costly engine repairs. Common symptoms include:
- Overheating: Coolant leakage into the combustion chambers can cause persistent overheating.
- White or Bluish Exhaust Smoke: This may indicate coolant or oil burning in the cylinders.
- Milky Oil Appearance: Contaminated oil appears frothy or chocolate milk-like, often due to coolant mixing with oil.
- Loss of Engine Power: Reduced compression can cause misfires and a noticeable drop in performance.
- Bubbles in Coolant Reservoir: Exhaust gases entering the coolant system create visible bubbling.
Causes of Head Gasket Failures
- Engine Overheating: Insufficient coolant or defective cooling systems increase the risk of gasket failure.
- Age and Wear: Over time, high mileage and repeated heat cycles weaken the gasket.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect torque or alignment can lead to premature gasket failure.
- Design Flaws: Certain engines are inherently more prone to gasket problems due to structural design issues.
Preventing Head Gasket Issues
- Regular maintenance, such as coolant and oil checks.
- Using manufacturer-recommended fluids to prevent corrosion and overheating.
- Addressing minor engine issues early to avoid compounding problems.
- Monitoring your vehicle for any warning signs and acting promptly.
Repair and Costs
Repairing or replacing a head gasket is labor-intensive, as it involves disassembling much of the engine. Costs range from $1,000 to $2,500, depending on vehicle type, engine complexity, and labor rates. While expensive, it’s significantly less than replacing an entire engine. Always seek professional assistance for diagnostics and repairs to ensure quality work.
By understanding the importance and maintenance of head gaskets, vehicle owners can extend the life of their engines and avoid costly repairs. If you suspect head gasket issues, consult a mechanic immediately to prevent long-term damage.