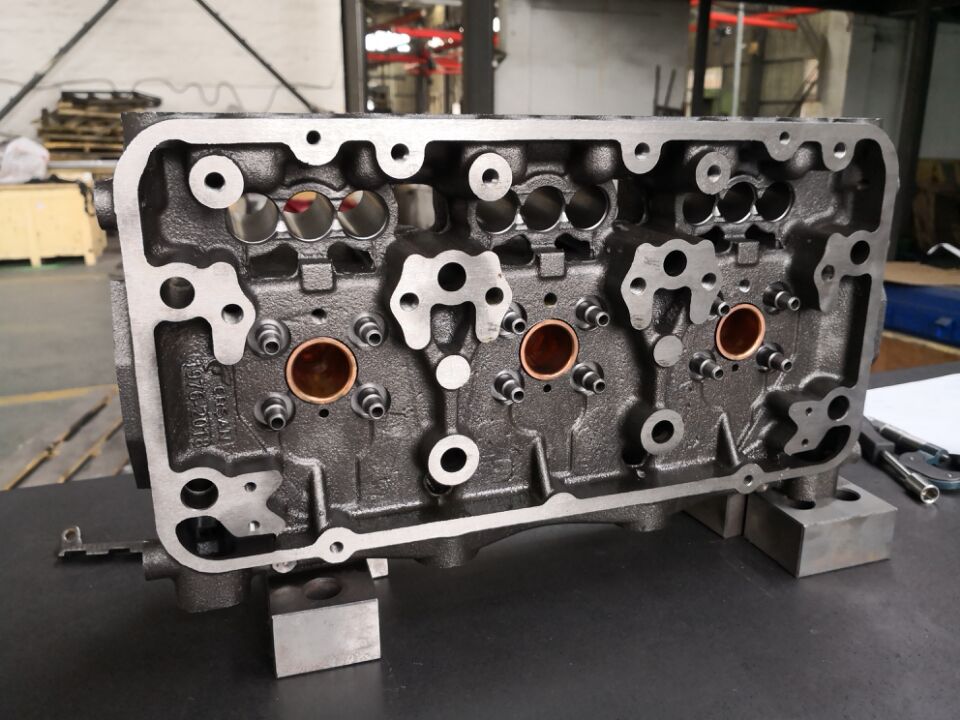
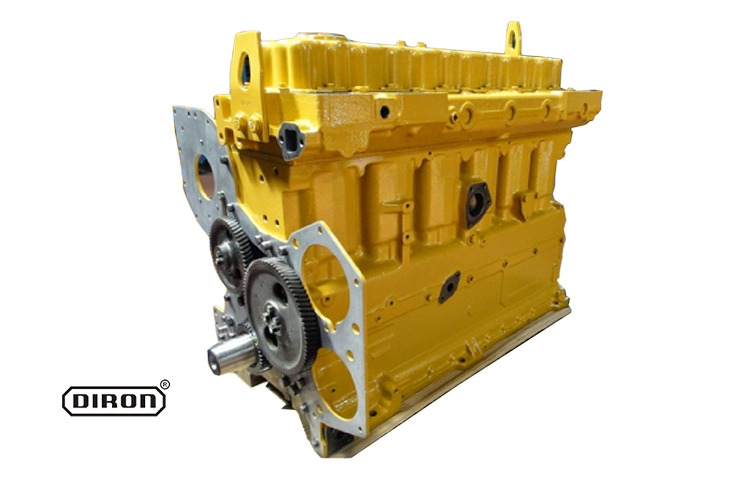
Diesel engines are renowned for their durability, efficiency, and power. Whether used in heavy machinery, vehicles, or generators, the diesel engine remains a key part of industrial and automotive sectors. In this article, we analyze the components of a diesel engine, breaking down its structure and explaining the role of each part.
What Is a Diesel Engine?
A diesel engine is a type of internal combustion engine where fuel ignition occurs due to the heat generated by compressed air, rather than using spark plugs. Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient and produce higher torque compared to gasoline engines, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Key Diesel Engine Components Explained
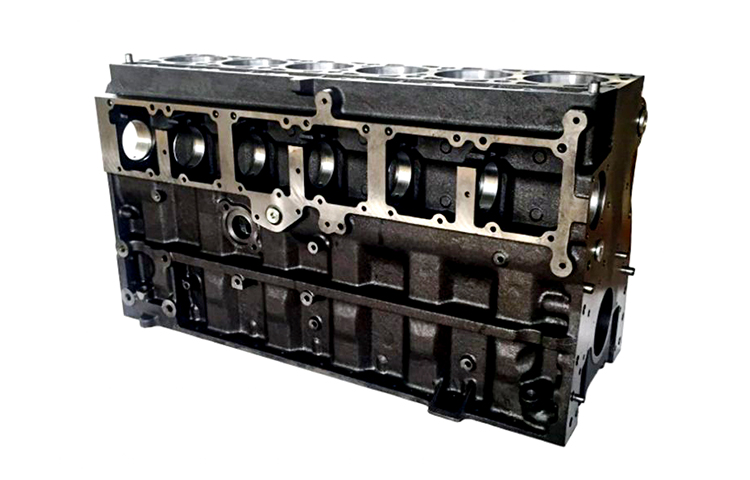

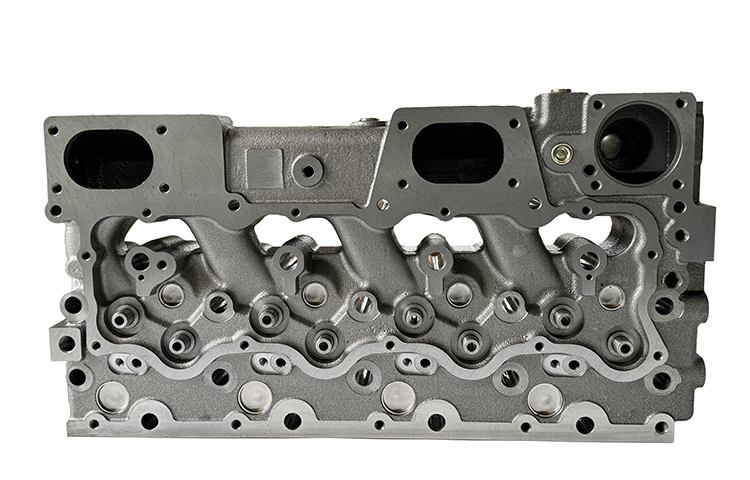


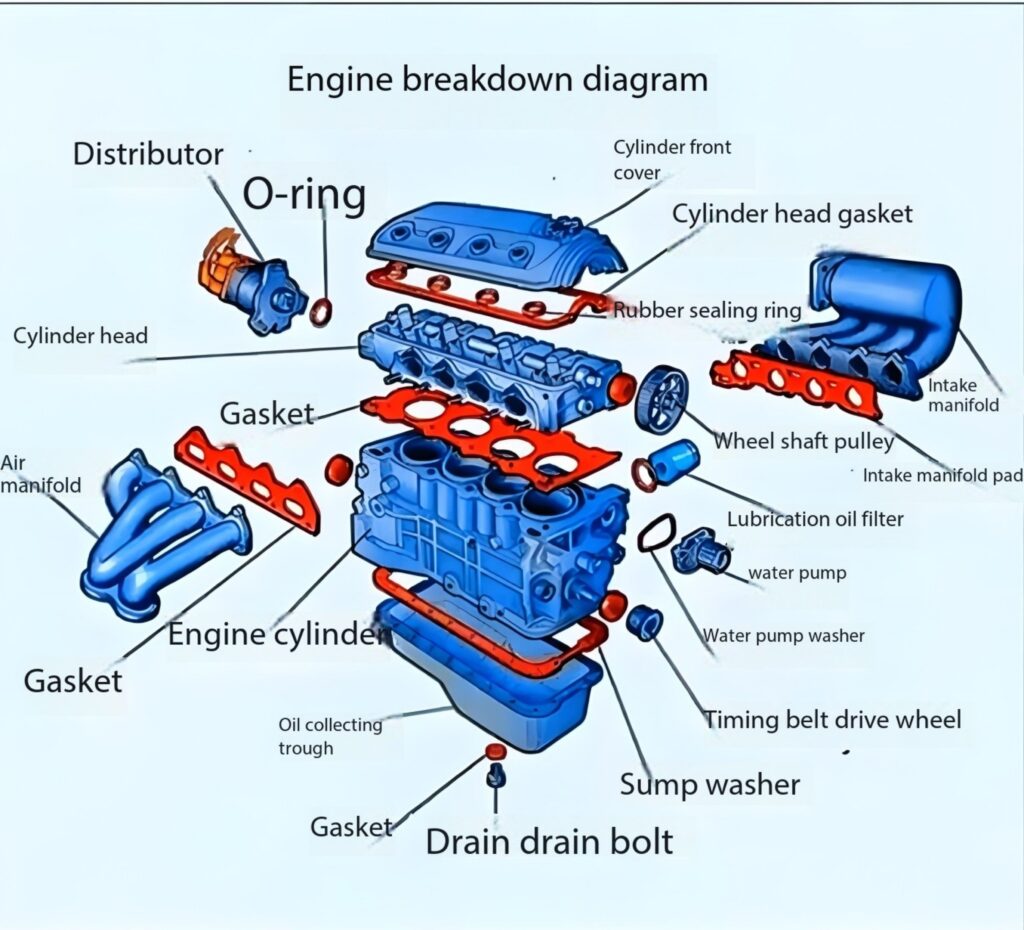
The diagram above provides a clear breakdown of a diesel engine, showing its main parts. Let’s dive into the key components and their functions:
1. Cylinder Head
The cylinder head is an essential part of the diesel engine. It sits above the engine cylinder and houses components such as the intake and exhaust valves, fuel injectors, and combustion chamber. It ensures proper sealing and helps direct airflow in and out of the engine.
2. Cylinder Head Gasket
The cylinder head gasket is crucial for maintaining a tight seal between the engine block and cylinder head. This prevents oil, coolant, and combustion gases from leaking, ensuring optimal engine performance.
3. Engine Cylinder
The engine cylinder is where the diesel fuel combusts. Pistons move up and down within these cylinders, converting combustion energy into mechanical power that drives the vehicle or machinery.
4. Intake Manifold
The intake manifold distributes air (or the air-fuel mixture) evenly to the engine cylinders. In a diesel engine, it primarily handles air intake to prepare for compression ignition.
5. Gaskets and Sealing Rings
Gaskets and rubber sealing rings play a vital role in preventing leaks of fluids like oil and coolant. They ensure tight seals between different components of the diesel engine.
6. Distributor
The distributor is part of the fuel injection system. In a diesel engine, it helps control the timing and distribution of diesel fuel to each cylinder for combustion.
7. Lubrication Oil Filter
The lubrication oil filter removes contaminants from the engine oil, ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear and tear on moving parts.
8. Water Pump
The water pump circulates coolant throughout the diesel engine, maintaining optimal temperatures and preventing overheating during operation.
9. Timing Belt Drive Wheel
The timing belt drive wheel synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring the engine’s valves open and close at the correct times.
10. Drain Bolt and Sump Washer
The drain bolt allows for easy removal of oil during maintenance, while the sump washer ensures there are no leaks at the drain plug.
How Does a Diesel Engine Work?
Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines rely on compression ignition. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Air Intake: The engine draws in air, which is compressed to high pressures.
- Compression: Compressing the air heats it to extremely high temperatures.
- Fuel Injection: Diesel fuel is sprayed into the hot, compressed air.
- Combustion: The fuel ignites spontaneously due to the high temperature.
- Power Stroke: The expanding gases push the piston downward, generating power.
- Exhaust Stroke: Combustion gases are expelled, and the cycle repeats.
Why Choose a Diesel Engine?
Diesel engines have several advantages that make them ideal for various applications:
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines consume less fuel compared to gasoline engines, offering better mileage.
- High Torque: They provide greater low-end torque, making them perfect for heavy-duty vehicles and machinery.
- Durability: Diesel engines are built to last longer, with robust construction and fewer maintenance requirements.
- Cost-Effective: While initial costs may be higher, the long-term savings in fuel and maintenance outweigh the investment.
Conclusion
The diesel engine is a powerful and efficient technology that powers industries and transportation worldwide. Understanding its components—like the cylinder head, gaskets, and intake manifold—is key to appreciating its functionality. With their unmatched efficiency and durability, diesel engines remain a cornerstone of modern engineering.
If you’re looking to learn more about diesel engines or require maintenance tips, stay tuned to our blog for in-depth guides and updates!